The “Little Brain In the Heart”
Slide 1.
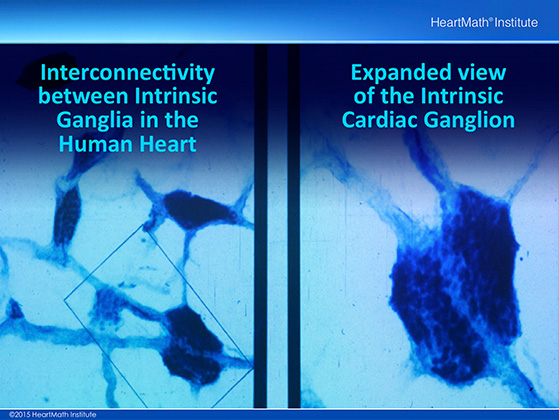
This is a microscopic picture showing the interconnectivity between cardiac ganglia in the human heart. The light blue thin structures in the image on the left are multiple axons coursing between and connecting the ganglia. The image on the right is an expanded view of the ganglia shown in the rectangular box in the image on the left.
Slide 2.
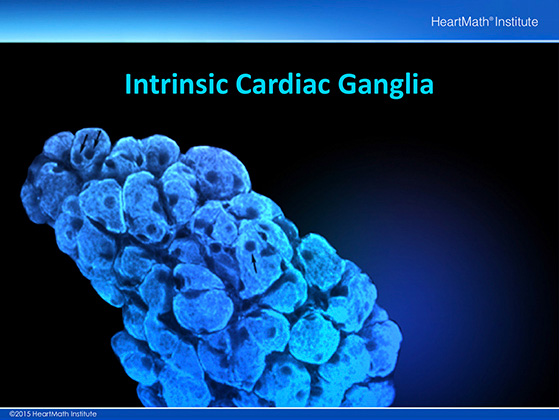
This is a highly magnified view of a cardiac intrinsic ganglia taken with a confocal microscope which is able to take images layer by layer and then build a 3D image. Ganglia are made up of groups of nerve cells (somata) that exist outside of the brain and spinal cord. Each of the smaller circular structures shown is the cell body of an individual neuron.

Slide 3.
This image represents a cross section through an intrinsic cardiac ganglion. In the center there is a mass of dendrites which interconnect individual neurons. This is the ideal structure for an independent neural processing unit.
Slide 4.
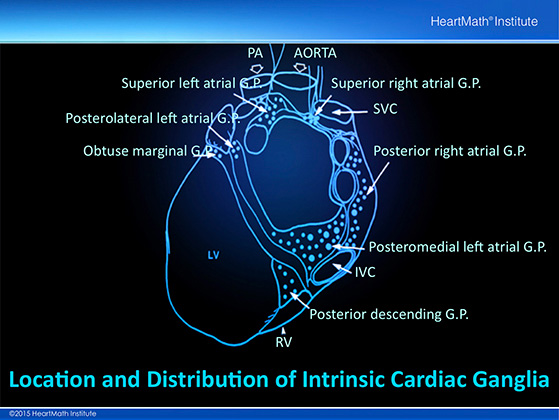
This drawing shows the location and distribution of intrinsic cardiac ganglia. Note how they are distributed particularly around the orifices of major vessels.

Slide 5.
This picture of intrinsic cardiac afferent neurons was taken with a confocal microscope. An afferent neuron is one that sends information to another neuron. These sensory neurons detect the local mechanical and biochemical changes that occur in cardiac tissue. They send this information to the rest of the intrinsic cardiac nervous systems and in many cases to the brain.
